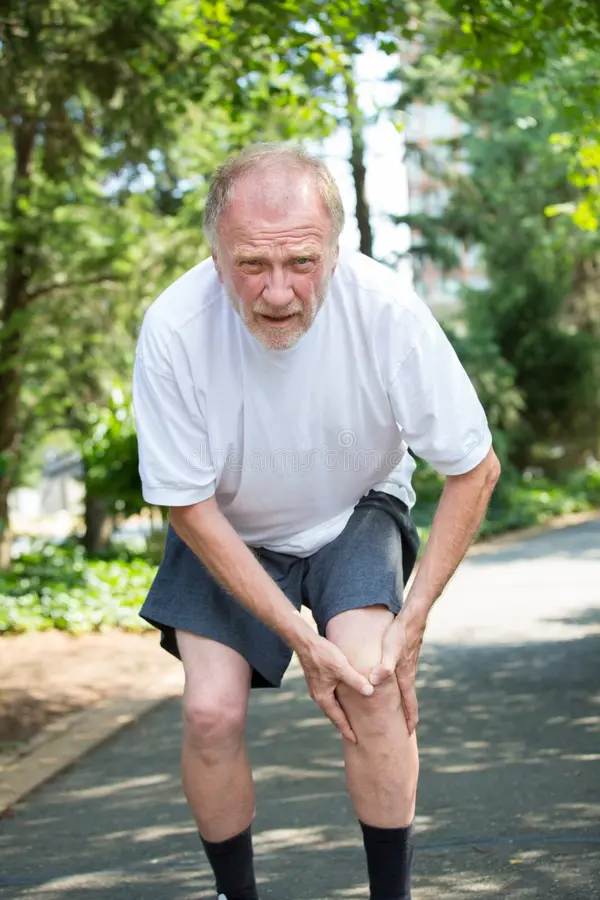
Knee pain is one of the most common complaints, especially among those dealing with arthritis. Whether it’s due to aging, injury, or an underlying medical condition, knee pain can significantly affect quality of life. Arthritis, a disease characterized by inflammation in the joints, is often the root cause of knee pain. Understanding the connection between knee pain and arthritis, the treatments available, and the best practices for maintaining knee health can help manage symptoms effectively.
Connection Between Arthritis and Knee Pain
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are two of the most common forms of arthritis that affect the knee joints. OA typically occurs as a result of wear and tear on the cartilage in the knee, while RA is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the synovial membrane surrounding the knee joints.
In both cases, the inflammation in the knee joint can result in pain, swelling, and stiffness, making movement difficult and painful. Over time, untreated arthritis can lead to joint deformity and loss of function, making it essential to seek treatment early.
How Arthritis Affects Knee Joints
Arthritis causes damage to the cartilage, the cushion between the bones in the knee joint. In OA, the cartilage wears away, leading to bone-on-bone friction, which causes pain and inflammation. RA, on the other hand, leads to the thickening of the synovial membrane and the production of inflammatory fluids, which can erode the cartilage and bones in the knee.
As arthritis progresses, the knee joint may lose its ability to move properly, resulting in limited range of motion and difficulty in performing everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and standing. In advanced cases, arthritis can cause joint deformities and even disability.
Medical and Home Remedies for Knee Pain Relief
For many people, managing knee pain caused by arthritis involves a combination of medical treatments and home remedies. Here are some options:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation. For severe pain, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for RA.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design an exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, which can help stabilize the joint and reduce pain.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs can help reduce swelling, while heat packs can improve blood flow and relax the muscles around the knee joint.
- Compression and Elevation: Using a knee brace or wrap can provide compression to reduce swelling. Elevating the leg also helps minimize fluid retention and reduces inflammation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on the knee joint. Even a small amount of weight loss can significantly improve symptoms in overweight individuals with knee arthritis.
Role of Knee Injections in Arthritis Treatment
Injections are often used to provide more immediate relief from knee pain caused by arthritis. Two common types of injections used in arthritis treatment are corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These injections contain powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can provide relief from swelling and pain for several weeks or months. They are particularly useful during flare-ups of arthritis.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Hyaluronic acid is a substance naturally found in joint fluids. Injections of hyaluronic acid help to lubricate the knee joint, reducing pain and improving mobility, especially in OA patients.
Exercises and Lifestyle Changes for Healthier Knees
Exercise plays a vital role in managing knee pain caused by arthritis. Strengthening the muscles around the knee can help protect the joint and improve mobility. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking can help maintain joint flexibility without putting excessive strain on the knees.
In addition to exercise, adopting a healthier lifestyle is essential:
- Diet: Eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin D can help reduce inflammation and support joint health.
- Stress Reduction: Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can also help alleviate pain and prevent flare-ups.
Conclusion
Knee pain due to arthritis can be debilitating, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and maintain knee health. Whether through medications, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes, there are several ways to improve quality of life for those suffering from arthritis-related knee pain.